Last week, we explored the meaning of website internationalization, which is the first step towards building websites that cater to the navigation preferences of a global audience. If the concept is new, we recommend reading that article first. Click here to access it.
What is Website Localization, and what it means to the executive search services industry?
When global businesses want to provide an intercultural user experience, designing web pages to communicate to a single overseas market, referred to as localization. The localized sites are created using the global template, keeping to its web design guidelines and adapting where permissible.
Localization is the integration of language translation, transcreation, image appropriateness, market-adaptation of services, process definition and regulatory compliance, and presenting what is considered a compelling offer of services in that locale.
Localized web pages in the form of ccTLD’s, subdomains and subfolders
If the website user prefers to interact with the website dedicated to their home country, in their own language, they would look within the global gateway that links to a separate regional and/or translated page, adapted to their geographic, cultural and linguistic preferences.
A global gateway is usually visible in the main menu or top bar, represented by a globe icon. It is a listing of language options or locations that links to a specific translated and/or regional web page.
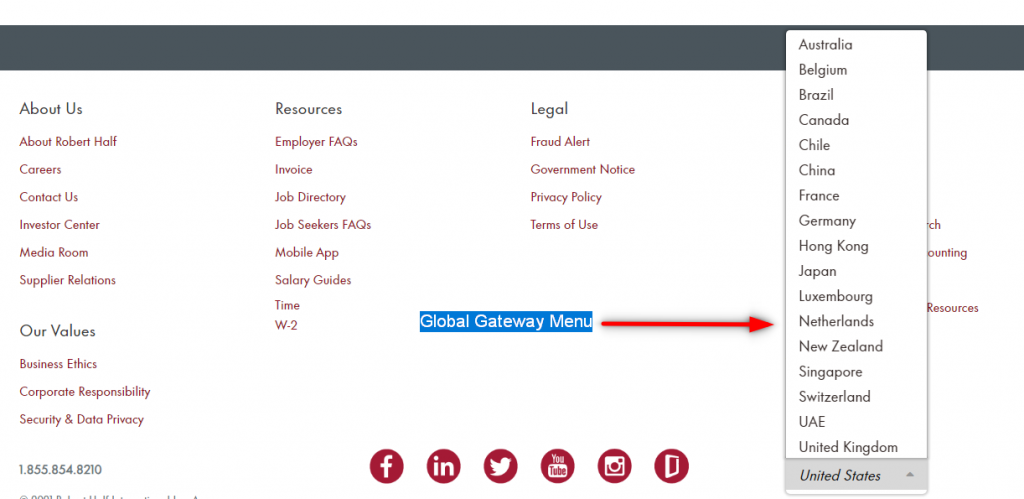
Figure 1: The global gateway menu on the website of Robert Half
The countries or languages listed within the global gateway should ideally be mentioned in the text format, rather than using flags. If it is strictly meant to offer translation, and nothing more, it makes sense to say, for example, ‘Spanish’, as multiple countries speak the language. This makes it easy for all Spanish speakers to choose the language option. By placing, for example, the flag of Mexico, the website restricts users to only one geography and drives off Spanish speakers from other countries. In this situation, sticking to text makes the interaction more intuitive and engaging.
As mentioned before, localization is the next step after language translation. A website that has reached this stage, following the best practice of intercultural web design, is now ready to move to the next step of website localization to interact intently with foreign markets.
ccTLD (country code top-level domain)
ccTLD’s typically refers to the target country for your website. For example, search engines understand that a domain that ends with .in is targeted to users in India. Many SEO experts strongly believe that Google and other search engines like Naver, Yandex or Baidu prefer to rank ccTLD websites in countries outside of the United States.
A good practice is to make sure that it is linked to the parent website, since most global visitors tend to prefer to visit here first.
There are certain countries that prefer visiting those websites specific to their region.
Example, Australians prefer to visit .com.au sites, Canadians prefer .ca, and the British prefer .co.uk. Arab countries like Saudi Arabia prefer to visit the source site, as they believe these sites are more reliable compared to the regional site.
Providing this option to choose between the source site and country specific URL is preferable, as this passes the control to the user to select the best experience.
Subfolder
A subfolder or subdirectory exists within the source website, and it holds its own design and content separately to support translation and localization efforts.
A notable benefit is that it eliminates the need to maintain multiple websites. However, from Google’s perspective, they essentially are different websites, thus helping the localized pages rank in the respective languages. Users can still easily reach these pages if they searched for the sites in their own language.
Example of subfolder formats –
www.executivesearchfirm.com/fr (meant for users in France)
www.executivesearchfirm.com/ca (meant for users in Canada)
Subdomain
Subdomains enables the setting up of multiple websites using a single domain.
Example of subdomain formats –
www.shop.executivesearchfirm.com
www.resources.executivesearchfirm.com
Usually, subdomains are used to promote shops or blogs separately from the main URL (primary domain), and many argue that this approach helps with improved SEO results. However, they operate as separate URL’s from the main domain, and can exist on their own if they are not linked back to the primary URL.
Choosing between these three structures is dependent on the preferences of the executive search firm, and want kind of experiences would best serve both – target audience and business goals.